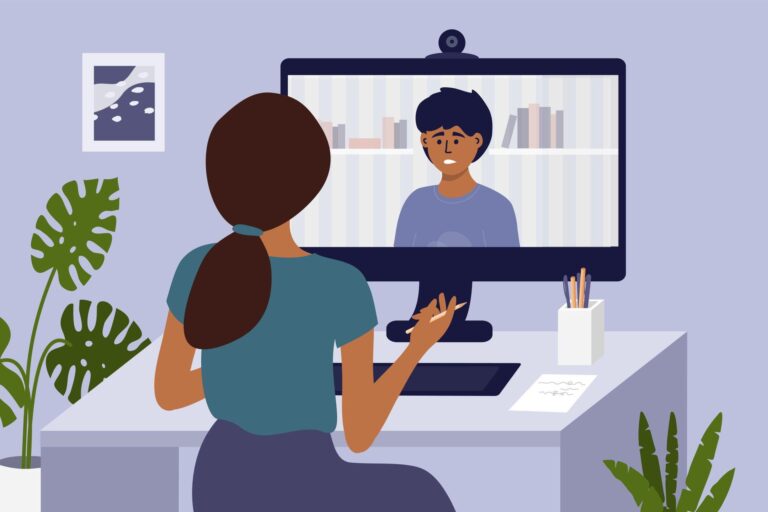
In an era marked by unprecedented technological advancements and an increasing awareness of mental health needs, teletherapy has emerged as a potentially transformative modality for mental health management. This article delves into the viability of teletherapy as a sustainable and effective approach to mental health care. By examining empirical data, expert opinions, and patient outcomes, we aim to assess whether teletherapy is poised to become the cornerstone of future mental health services. As we navigate this complex landscape, key considerations include accessibility, efficacy, regulatory challenges, and the role of technology in facilitating therapeutic interventions. Join us as we explore the multifaceted dimensions of teletherapy and its potential to redefine the paradigms of mental health management.
Current Landscape: Understanding Teletherapy’s Rapid Growth
The surge in teletherapy has been remarkable in recent years, driven by several critical factors. Advancements in technology such as high-speed internet and reliable video conferencing tools have made virtual sessions more accessible. Additionally, the global pandemic necessitated social distancing, pushing both practitioners and clients towards remote mental health services. The convenience and flexibility offered by teletherapy mean that clients can receive support from home, eliminating the need for travel and removing geographic barriers. This has particularly benefited individuals in rural or underserved areas where mental health services were previously limited.
- Increased access to licensed professionals
- Reducing stigma associated with visiting a therapist
- Cost-effectiveness for both providers and clients
For a clearer understanding, let’s look at some key statistics:
| Year | Teletherapy Usage (%) |
|---|---|
| 2019 | 11% |
| 2020 | 44% |
| 2021 | 55% |
As illustrated, the percentage of people using teletherapy has considerably increased, and it shows no signs of slowing down. The convenience of teletherapy could very well shape the future landscape of mental health management.

Technological Advancements: Enhancing Accessibility and Engagement
Recent technological strides have made it possible for mental health care to be more accessible and engaging than ever before. With the advent of teletherapy, individuals can connect with mental health professionals from virtually anywhere. This means that geographical barriers can be eliminated, providing support to those in remote or underserved areas. Additionally, teletherapy offers a level of convenience that traditional face-to-face therapy often cannot match. Patients can schedule sessions that fit into their busy lives, reducing the problem of missed appointments.
Key Advantages of Teletherapy include:
- Flexibility: Clients can choose the time and place for their sessions.
- Accessibility: Ideal for those living in rural areas.
- Affordability: Often less costly than in-person visits.
- Reduced Stigma: Can be more private, thus encouraging participation.
| Aspect | Traditional Therapy | Teletherapy |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Fixed | Flexible |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Accessibility | Limited | Wide |

Efficacy and Outcomes: Comparing Teletherapy with Traditional Methods
When exploring the effectiveness of teletherapy in comparison to traditional face-to-face therapy, several important factors come into play. Research has shown that teletherapy can be just as effective as in-person therapy for a variety of mental health conditions. These include, but are not limited to:
- Depression
- Anxiety disorders
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Substance abuse
Furthermore, teletherapy offers unique advantages such as increased accessibility, reduced stigma, and greater convenience for patients, all of which contribute to its efficacy.
Outcome studies comparing both modalities have utilized various metrics such as patient satisfaction, symptom reduction, and therapy adherence. The table below highlights key findings from recent studies:
| Metric | Teletherapy | Traditional Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Patient Satisfaction | High | High |
| Symptom Reduction | Comparable | Comparable |
| Therapy Adherence | Greater | Variable |
These findings underscore that teletherapy is a viable option with comparable outcomes to traditional therapeutic methods, and in some aspects, it even excels.

Implementation Strategies: Best Practices for Integrating Teletherapy into Mental Health Services
To effectively integrate teletherapy into mental health services, it’s crucial to follow several best practices. Start by ensuring your technology infrastructure is robust. This includes high-quality video platforms, reliable internet connections, and secure, HIPAA-compliant software to protect patient information. Staff training is equally essential; make sure that all team members are comfortable and proficient with the new technologies before they start using them for patient care.
Consider the importance of maintaining patient engagement and satisfaction. Some strategies include:
- Regular Follow-ups: Schedule regular virtual check-ins to monitor progress and make necessary adjustments.
- User-Friendly Platforms: Opt for platforms that are easy for patients to navigate, ensuring that tech challenges don’t become barriers to care.
- Personal Touch: Incorporate personal touches such as sending digital resources after sessions or using email reminders.
Providing clear guidelines and setting expectations from the outset can also mitigate any uncertainties and help make teletherapy a more seamless experience for both practitioners and patients.
| Strategy | Key Actions |
|---|---|
| Infrastructure | High-quality video, secure software |
| Staff Training | Proficiency with new tech before patient use |
| Patient Engagement | Regular follow-ups, user-friendly platforms |
Q&A
Q: What is teletherapy, and how does it operate?
A: Teletherapy, also known as online therapy or e-therapy, is a method of delivering mental health services via digital platforms such as video conferencing, telephone calls, or messaging systems. It operates through secure, encrypted communications, allowing patients to connect with licensed mental health professionals from remote locations.
Q: What advantages does teletherapy offer over traditional in-person therapy?
A: Teletherapy provides several advantages, including increased accessibility for individuals in remote or underserved areas, greater convenience in scheduling, reduced travel costs, and enhanced privacy. It also offers flexibility for individuals with mobility issues or demanding schedules.
Q: Are there specific technological requirements for teletherapy?
A: Yes, effective teletherapy typically requires a stable internet connection, a computer or mobile device with a camera and microphone, and access to secure, HIPAA-compliant communication platforms to ensure confidentiality and privacy.
Q: How does teletherapy address concerns related to data security and patient confidentiality?
A: Teletherapy services adhere to stringent data security protocols, such as encryption and secure servers, to protect patient information. Providers use HIPAA-compliant platforms that ensure adherence to federal privacy regulations and maintain patient confidentiality.
Q: Are there limitations or challenges associated with teletherapy?
A: Some limitations of teletherapy include potential technology barriers, such as poor internet connectivity or lack of access to necessary devices, and the reduced ability of therapists to interpret non-verbal cues. Additionally, teletherapy may not be suitable for all conditions, particularly severe mental health crises that require immediate, in-person intervention.
Q: What evidence exists regarding the effectiveness of teletherapy compared to in-person therapy?
A: Research indicates that teletherapy can be as effective as traditional in-person therapy for a range of mental health issues, including depression, anxiety, PTSD, and substance use disorders. Several studies have shown comparable outcomes in symptom reduction and patient satisfaction between the two modalities.
Q: How has the COVID-19 pandemic influenced the acceptance and adoption of teletherapy?
A: The COVID-19 pandemic significantly accelerated the adoption of teletherapy as a necessary means to continue mental health care while adhering to social distancing guidelines. This period demonstrated teletherapy’s viability and led to increased acceptance among both providers and patients, as well as policy adaptations to facilitate broader access.
Q: What future developments are anticipated in the field of teletherapy?
A: Future developments in teletherapy may include advancements in artificial intelligence for personalized treatment plans, the integration of virtual reality for immersive therapy experiences, and broader insurance coverage. Additionally, ongoing research is expected to refine best practices and improve teletherapy efficacy across diverse populations.
Q: What role does teletherapy play in the broader landscape of mental health management?
A: Teletherapy plays a critical role in expanding access to mental health services, particularly in areas with a shortage of mental health professionals. It also complements traditional in-person therapy by offering an alternative for follow-up sessions, ongoing support, and crisis intervention, thereby enhancing the overall mental health care continuum.
The Way Forward
teletherapy presents a promising avenue for the future of mental health management. Its potential benefits, including increased accessibility, convenience, and flexibility, position it as a significant advancement in the mental healthcare landscape. However, challenges such as technological barriers, privacy concerns, and the need for personalized, face-to-face interaction must not be overlooked. Ongoing research, policy development, and technological innovations will be key to addressing these concerns and optimizing the efficacy of teletherapy. As the field continues to evolve, stakeholders must collaboratively navigate these complexities to ensure that teletherapy becomes a robust, viable component of comprehensive mental health care strategies. The future of mental health management may very well hinge on our collective ability to integrate traditional and digital modalities in a balanced and effective manner.


